Robotic process automation or RPA is a powerful tool that can be used as part of the commercial banking toolbox to streamline and automate a number of routine, manual banking processes, or sub-processes. In fact, it can reduce new account opening time by 30 percent and cut error rates to zero. Did you know that the lack of standard processes can prevent up to 60 percent of potential banking operations RPA use cases from being implemented? In this blog post, we’ll walk you through the five steps of how we make RPA work in your commercial banking operations. We’ll also give you an in-depth case study to help you understand exactly what RPA in your bank can do.
What is RPA implementation in commercial banking operations?
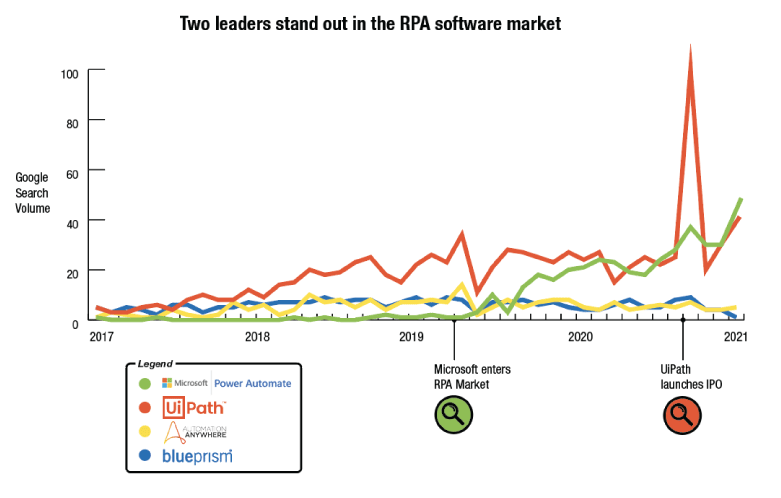
RPA implementation in banking operations and commercial lending is defined as the use of desktop-level automation applications, like Blue Prism, Automation Anywhere, or UiPath, to automatically process banking data transcriptions that must occur in between systems for bank processes. For example, when a customer opens new business bank accounts or applies for a loan after RPA implementation, back office banking staff can expect drastically reduced human work effort needed to support commercial banking processes that traditionally require manual moving of data from applications into core systems to complete transactions.
In the past, such banking operations automation was limited to core system integration; integration could only happen at the code level. But with commercial banking operations RPA, use cases can now be implemented at the presentation level or keystroke/mouse-click level, with no conventional coding—or knowledge thereof—required. When properly implemented, RPA in commercial banking operations weaves together multiple core system fields, cloud-based software fields, and desktop applications like Excel into a single and automatic process – without any underlying architecture change.
In commercial banking operations, RPA does not mean that robots are making any decisions. Quite the opposite. RPA in banking involves automating the simplest, most repetitive administrative and clerical data work tasks at the keystroke level.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZMdXF9Lbgfk
Business processes in commercial banking operations that RPA use cases can be applied to include:
- Commercial deposit operations.
- Commercial loan and line-of-credit processing for new business and renewals.
- Small business loan administration.
- Payment processing and merchant services.
- Loan servicing.
- Treasury and cash management.
Most commercial banking core system implementations like Pega, Fiserv, and SAP Loan Management fall short of the promise of straight-through processing—too much sizzle and not enough steak. Commercial banking operations RPA focuses on the sub-processes and manual work processed outside of these systems, integrating work steps that core systems were never designed—nor able—to address.
Example Case Studies of RPA Implementation in Commercial Banking Operations
Commercial banking operations has numerous repetitive administrative tasks and manual processes that occur outside of legacy systems. This fact makes them a natural choice-point for implementing RPA.
Other commercial banks may not be willing to tell you how much they’ve saved by implementing RPA in their organizations. Below are three case studies of RPA in banking operations that tell the tale.
RPA Implementation in Banking Case Study 1: Global Commercial Bank Embraces RPA for Investment Cost Compared to Return Value
A global bank’s innovation leader has been championing RPA for four years in his firm. Anywhere from 30 percent to 70 percent automation has been realized, depending on where it was introduced.
RPA implementation in Banking Case Study 2: UK Bank Reduced Turnaround Time by 35%
A leading UK bank deployed RPA to process transactions and sweep operations, slashing manual labor by more than a third. Simultaneously, bank operations management increased productivity by 20 percent, significantly improved accuracy, and sizably reduced full-time equivalent resources.
RPA in Banking Case Study 3: U.S. Retail Bank Achieves 100% Accuracy
Using RPA in the bank account opening process, operations management extracted data from input forms, feeding it into a variety of host applications automatically. The bank succeeded in eliminating the error-prone, time-consuming manual data entry process. Results included reducing account-opening time by almost 30 percent.
A detailed banking RPA case study example in commercial lending operations
A real-life example of RPA in commercial banking operations will paint a vivid picture of the potential gains your company can realize. Let’s look at an example that shows how RPA was used to automate work that takes place outside of core lending systems for opening a new commercial line of credit.
The pre-RPA implementation commercial lending process is 75 percent manual, performed by a commercial loan processor in the back office—a fellow we’ll call “Joe.” This slice of a “day in the life” of Joe goes something like this:
- Joe receives the final commercial loan onboarding package from Underwriting and other supporting documents from the loan officer via email.
- Joe opens the loan processing system to ensure all the information from the loan officer and underwriting is in the loan processing system and complete.
- Joe reconciles, copies, and pastes all the missing data from the loan officer’s email into the loan processing system.
- Joe then copies and pastes all missing data from underwriting into the loan processing system.
- Joe prepares the loan file for closing by checking the Secretary of State website for confirmation of loan applicant business status.
- Joe manually sends a standard template email to loan operations for loan booking once all the paperwork is in good order.
The above process takes 45 minutes per loan, but it’s only part of what Joe has to do as a matter of routine, day in and day out.
You might be wondering: “Why are my commercial loan processors doing so much manual work, when I’ve bought core commercial banking management systems that have already sold me ‘straight-through processing’ seven times already?”
Unfortunately, all large commercial banking departments today are facing the same challenges that you are. RPA is tailor-made to provide non-code solutions to banking automation gaps that others have not been able to deliver.
With RPA, and his new trusty robot as his sidekick, Joe finds that his workday is more interesting and exciting. Let’s review Joe’s work process once the robot has been installed, with the steps impacted by banking RPA shown in italics and bold:
- Joe receives the final commercial loan onboarding package from Underwriting and the loan officer via email.
- The RPA bot opens the loan processing system to ensure all the information from the loan officer and underwriting is in the loan processing system and complete. This process occurs automatically once Joe clicks “start the process”.
- The RPA bot scans received document fields and pulls anything that is missing onto the core loan processing system. Joe no longer has to copy that data field by field, or reconcile, copy, or paste data from the loan officer’s email into the loan processing system.
- The RPA bot then copies and pastes all missing data from underwriting into the loan processing system. Joe doesn’t have to do this anymore, either.
- The RPA robotic banker opens his web browser, logs in to the Secretary of State website, and checks to make sure the loan applicant is still a registered business.
- Once the Secretary of State confirmation is complete, RPA sends an automatic Outlook email to loan operations to book and disburse the loan. Joe doesn’t have to do this anymore—the robot does it for him, too.
- With RPA in place, Joe is now free to work on more interesting and important tasks—ones that increase his job satisfaction and help him advance in his career, all while saving the bank money!
It’s pretty interesting, isn’t it? Banking RPA really does work. Like anything else, you have to put in some work to get it going, which we’ll discuss next.
How to implement robotic process automation in banking operations
Robotic process automation in your banking operations won’t just analyze your processes and implement itself, no matter how “intelligent” people my try to convince you that robots or any kind of artificial intelligence can be. Thorough process analysis at the “in the weeds” level must be undertaken to understand where installing robots yields the most benefit to your business. Below we will walk you through how to implement RPA in your bank.
Step One: Identify practical use cases commercial banking RPA implementation
Processes with high levels of repetitive data transcription work are the best candidates for your first commercial banking RPA project. Thus, identifying a small, manageable list of processes that would benefit from being automated—your potential project scope—is the first step. All banking workstreams are not created equal when it comes to RPA use case implementation.
Does the work that you’re considering for banking RPA implementation require a lot of human decision-making? Then it’s probably not a great candidate for RPA. Processes with high levels of customer interaction and human decision-making can be set to the side.
We suggest starting your banking use-case analysis in loan processing operational areas where data is being moved and reconciled by back office staff of your bank—activities that happen day in and day out. Selecting a few banking work streams that have simple, repetitive steps is the best way to start, as you’ll minimize your risk and maximize your buy-in that way. You may learn a few important lessons along the way, simultaneously gaining support for rolling out RPA to your entire department.
Step Two: Determine baseline commercial banking operations cost to calculate the total benefits realized from RPA implementation
Once you have determined the scope of your pilot project, it’s time to identify a baseline cost of banking operations. Measuring your initial operating costs and comparing them to your reduced post-implementation operating costs is one of the most important steps. In fact, it’s a requirement for keeping the project going and maintaining stakeholder buy-in.
How do you determine a baseline cost for a commercial banking RPA implementation project? Take the scope you have outlined above and pay a visit to your HR department manager. Work with them to figure out what each banking employee in the affected departments costs, fully loaded with benefits. Then, calculate an hourly cost, and extrapolate to determine what the cost savings from banking RPA on a minute-by-minute basis at scale is.
Step Three: Create banking RPA implementation use cases—all the way down to the mouse-click level
Documenting banking processes down to the mouse-click level sounds like a lot of work. Because it is! Having collected your baseline cost data, it’s now time to map the processes. That’s right—and it’s actually an arrow straight out of the lean six sigma quiver. It’s the most effective way for you to identify opportunities and use cases for RPA in commercial banking. At The Lab, we prefer to use process-mapping software like Microsoft Visio to represent the processes in scope visually. We also use a stencil such as the BPMN 2.0 stencil (Business Process Model and Notation), since it’s most widely accepted as the industry standard for such work.
The only way to make banking RPA use-case development succeed is to observe a commercial banker at their desk for a few days, notebook or laptop in hand—or lap. Take extremely detailed notes of every keystroke and mouse-click within all the applications you would like to automate. It’s important to observe multiple commercial banking workers for a few days, one at a time—enough to get a good sample size. If you are undertaking a department-wide initiative, plan on observing 50-500 workers and then scaling up. Here at The Lab, we do this type of “day in the life” observation for you in one of two ways: using screen-sharing software like GoToMeeting or WebEx, or face-to-face. Many organizations prefer the former route, since remote observations via screen-sharing significantly lower the project costs.
Step Four: Standardize commercial banking operations processes before or during RPA implementation
Why is standardizing the workflow before or during implementing commercial banking operations RPA so important?
Picture a robot on a factory floor welding pieces of metal together. The robot always welds Spot X before Spot Y, and welds Spot Y before it welds Spot Z, allowing it to move quickly and precisely. In fact, all the robots on the assembly line floor doing the same job are programmed identically, welding spots X, Y, and Z in the same order.
Similarly, you must standardize the workflow for your commercial banking operations processes before RPA is implemented. If Joe copies and pastes data in a different order than Joanna does, and Sam copies and pastes the same data in yet a third order, you’ll want to choose one standardized way of doing the job before or during RPA implementation. Waiting until afterward will only increase your costs, and you’ll fail to realize all the potential benefits that RPA in commercial banking has to offer.
Step Five: Talk to The Lab for RPA Implementation in Your Bank
RPA implementation in commercial banking is becoming more popular all the time. One question you might ask is whether to hire an RPA vendor to implement it, or do it yourself—your classic “make or buy” decision.
Whether you decide to hire an RPA vendor like The Lab or do it yourself, you can realize significant gains towards increasing your productivity rates—by following the five steps recommended in this article. Contact us if you want to get a head start today.
For 2021: We have updated our bank client offering. Much of these findings and implementation results can be reviewed in the 3-part-series of “Big Rocks for Banks” below. Find out how to strategically lower costs, increase operating leverage, improve customer experience, and automate what previously wasn’t automatable in your bank.
Find them all here: