How to Automate Your Insurance Claims Operation in 2026
Learn how “digital workers” can handle at least half of your carrier, brokerage, or MGA/MGU insurance operations
What are “digital workers”? And how can they help you, as an insurance executive, to automate your operations? What about “bots”? Where do they figure in the world of brokerages, carriers, and agencies such as MGAs and MGUs?
If you, your technology leads, and internal improvement teams are wondering about where to start when it comes automation in insurance, you’re not alone. There’s a ton of hype floating around the insurance industry these days, with buzzy terms like “agentic AI” and “large language models” or LLMs and “generative pre-trained transformers” or GPTs seemingly everywhere. Where should you begin? What, precisely, should you automate in insurance?
The answers can be hard to come by; AI firms are biased around their own software (which is, after all, what they’re selling). And they tend to focus on the theoretical more than the practical.
Fear not. In this article from The Lab, we will take a chainsaw to all of the jargon. We’ll cut through all of the marketing clutter. We’ll help you understand what automation in insurance actually is—and how you can put it to use for the maximum value in your carrier operations, brokerage, or agency.
And here’s an enticing bottom-line benefit for you, to keep you reading this long-form explainer article: You can automate your insurance operation, with “digital workers” performing at least half of your daily processes… and do it only 6 – 12 months.
Insurance Digital Workers
What are “digital workers” in insurance?
What’s a “digital worker” in insurance? And what about artificial intelligence or AI? What’s the difference?
They’re pretty much the same. For the purposes of this article, “digital worker” is an umbrella term: it will include all the hyped terms like AI, agentic AI, and so on. Indeed, one insurance business may have a different definition of “agentic AI” than another; the same applies to robotic process automation or RPA in insurance. Widen this view beyond insurance, and the differences become even more pronounced. And that’s not just how the verbiage or descriptors are applied; it’s how different businesses apply the technology, too.
In this article, we’re going to be refreshingly technology-agnostic. We’re not going to pitch any given platform or vendor or compare their specific features. Rather, we’ll tell you what the different advances in business-process automation mean in insurance, and what they can do for your business.
As we’d noted above, this article is for insurance executives, as well as their internal improvement teams and business-unit/technology leads. If you represent any one of these three audiences at your insurance carrier, brokerage, or MGA/MGU, be sure to share it with the others.
Agentic AI
What is agentic AI in insurance?
For every buzzy technology, there’s an equally buzzy (if confusing) acronym. Let’s clarify all the hype for you.
First of all, “agentic,” as in “agentic AI,” simply means “able to take action.” That is, it’s AI that has “agency”: the ability to do something.
Now that you know that, you can see how “agentic AI” can orchestrate a lot of other technologies. These include:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to insurance bots which perform tasks, using a given system in your insurance business (such as your agency management system, CRM, claims-processing systems, contact-center systems, etc.). And RPA gets its instructions from the LLM:
- Large Language Models (LLMs) typically reside upstream of RPA. They can understand input that’s either written or spoken. They translate plain English into instructions for the RPA mentioned above. They can understand a complex task and define the actions which the RPA (and other technologies) must execute.
- Application Programming Interface (API) is a set of rules which allow one software platform to interface (or “talk”) with another. For example, you could integrate intelligent document processing (described below) with your claims-processing system by using an API. That’s a powerful combination of automation and AI processing in insurance.
- Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) refers to technology which can “read” information—either free-form text or hand-writing— from all kinds of different documents. IDP is impressive; it can, for example, recognize fields inside different kinds of PDFs, often without the need to “train” it to learn where the fields are. So it can, for example, be used to “read” input from reports from different carriers which carry similar fields of information, but are formatted completely differently from one another.
So what do you get when you combine agentic AI, APIs, IDP, RPA, LLMs, and more? “Digital workers,” that’s what. They’ll let you process and automate a ton (remember: at least half) of the activities that you’ve been doing manually forever in your insurance brokerage, carrier, or MGA/MGU.
It’s helpful to think of digital workers, in many ways, like people. They can review and ingest input. They can plan and perform tasks. So they give your insurance business more capability—and even more, as they expand into more of its processes.
As should be pretty clear by now, you don’t want to implement just one of these technologies. You want to orchestrate them together. The resulting effect is synergistic: far more than the sum of its parts.
Imagine what kind of future-state you can create with digital workers in insurance: They can handle massive areas of work… way more than people or even people with helper “bots” at their side. Which might have you wondering: Which tools and technologies are available…
Insurance Automation Cost
How much does it cost to automate an insurance business?
This is the point at which most insurance executives brace themselves for sticker shock. But there’s good news: You won’t need a costly rip-and-replace of your tech stack; nor will you really need to spend terribly much to introduce these technologies into your insurance operation.
License fees for the technologies we’d mentioned above are typically nominal. Many vendors have pay as you go pricing. Others offer basic per-digital-worker-seat subscriptions. In other words, most will let you get started without big up-front fees.
It gets better. You needn’t buy a whole new system; you can, instead, just layer the new tech onto your existing stack. Some products are nearly free. And apps like Power Automate are bundled with every MS e365 license.
Insurance Automation Prerequisites
How quickly can you automate your insurance claims operation?
The speed at which you can automate your insurance brokerage, carrier, or agency operation (which includes the amount of errors and other speed bumps you encounter) is wholly dependent on one factor: Standardization.
You can’t realistically get the benefits of automation in insurance until all of your information is standardized. You can’t have years’ worth of information simply living inside your employees’ heads as tribal knowledge or rules of thumb. Similarly, you can’t automate if your training manuals and SOPs are outdated… if they even exist.
So the big prerequisite to automation in insurance is standardizing. You’ll need to input, document, analyze, and standardize all of that disparate data. Then it can be folded back into the process—and be ready for your upcoming digital workforce.
There are three steps to preparing for automation. They are: Building a future state process map, gap-testing that map against your current state, and prioritizing your findings.
Here’s more detail for each of those steps:
Insurance Automation Prerequisite Step 1:
Create a process map of your future state
At this point, don’t worry about the how. Just concentrate on the what. That’s what makes this step the easiest of the three. So don’t worry about how you’ll get to that future state of automation in insurance. Just concentrate one what you’d like your digital workers to do for you.
Sketch out the ideal future state, with all of the sought-after standardization improvements, analytics, and of course, automations. You’ll want your future state process map to include:
- All of your insurance business’ workflows and process steps
- Plans for future automation, including:
o RPA/digital workers
o AI, agentic AI
o Extended functionality of different systems - Prerequisites for standardization, including:
o Data structure and format
o Quality of data intake
o All human review and intervention - Improved analytical capabilities, including:
o Targets and thresholds
o Metrics such as KPIs and KRIs
o Standard insights and actions
Far too often, the very activity of process-mapping the future state of an insurance business becomes unnecessarily complex. Why? It happens, all too easily, when insurance executives keep comparing their present state to the future state they’re attempting to map.
Don’t fall into that trap. Design your future state from a blank sheet; disregard the current state. It seems counterintuitive, but doing so will make the process go smoother. And we’ll work on the current-state map after the future state has been designed.
For insurance carriers, brokerages, and agencies that are still struggling to map out their future state as a prerequisite to automation and onboarding digital workers, you can always contact The Lab. With the help of our Knowledge Base, we have already created templates for the ideal future state for any insurance brokerage, carrier, or MGA/MGU.
Insurance Automation Prerequisite Step 2:
Find the gaps between your future and current states
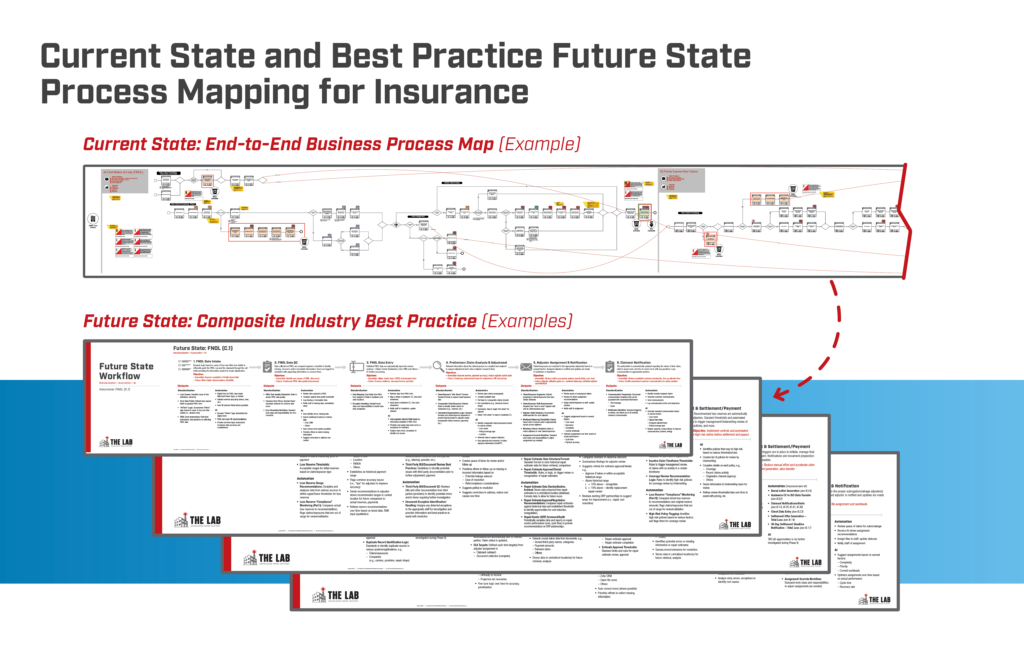
Now that you’ve successfully completed Insurance Automation Prerequisite Step 1 and have your future-state goals in hand, it’s time to gap-test them against your current state. This is when we’ll identify prerequisites for standardization in your insurance business. You’ll want to uncover which activities, tools, and work-flows will need to be changed, or added, to get your insurance business to the future state you’ve depicted.
Just as in Step 1, this step can be refreshingly liberating: Don’t worry if it’s possible to bridge the gaps that you find. Just list the gaps. You’ll want to simply compare the newly-produced future-state map to your current-state processes; you’ll also want to compare them to industry best practice. This will include things like:
- Automation and AI prerequisites
- Data structure and format
- Data-intake quality
- Existing automation capabilities
- Workflow design (e.g., exception detection, handling)
- Performance management capabilities
Again, don’t worry if you can’t bridge the gaps at this time. Just detail what they are—they could be something as simple as a checklist for a “bot” to use during its automation, or making your data more “automation-ready.” We’ll be talking about that shortly.
Insurance Automation Prerequisite Step 3:
Start with the biggest impact, and work your way down
Take your actions from Step 2 and re-order the list in terms of priority—with the biggest and broadest impact at the top.
What does “broad impact” mean in the context of automation in insurance? Automation impact in insurance is defined as occurring “both upstream and downstream of the automation itself, where it can deliver the most impact from end to end.”
Once you complete this step, you’ll have, in hand, a to-do list for attaining the automations of your insurance organization’s future state. In other words, it’s a road map for bringing digital workers on-board.
Your choice of automations in insurance, incidentally, isn’t limited to the list you’d just created and prioritized. The Lab’s proprietary IP Knowledge Base features over 500 time-tested automation use-cases to choose from. See our catalog of the most popular automations for insurance here.
The Lab has lots of resources to accelerate your insurance business’ automation journey. To help you roll out, execute, and scale your initiative, The Lab has:
- Catalogs for prioritizing insurance automation use-cases
- Development frameworks for employing scalable code
- Dashboards which you can deploy to monitor the performance of your insurance organization’s digital workers
- Standardized requirements-documentation templates
- Project management tools & standards
- Process-improvement guidelines
- Maturity models to help facilitate your company’s capability development
- Recommended training courses for your internal resources
Using the insurance automations you’ve selected from The Lab’s Knowledge Base and bot catalog, as well as those which you’ve ID’ed from mapping out your automation future state, you’ll reduce the amount of time and effort needed to develop each bot/digital worker.
But the biggest value lies in end-to-end implementation of digital workers and AI across your insurance brokerage, carrier, or agency; that’s how you’ll reap maximum ROI and value.
Insurance Automation Pitfalls
What are the two most common pitfalls when automating insurance operations?
Insurance Automation Pitfall 1:
Listing incremental, and not collective, benefits
Insurance program managers often define goals arbitrarily, for example: “Each insurance bot must save at least 500 hours of manual labor every year.”
The problem here is the definition, because all of those hours are upstream. Writing thresholds like these overlooks the huge downstream benefit, where the “upstream bot” enables other automations which can easily re-capture thousands of hours of effort each year.
How, then, do you avoid Pitfall 1 in insurance automation? Create more meaningful goals that are broader in scope. Ask, instead, questions such as: “What percentage of the entire business process is going to be performed by a digital worker?”
Remember, the more you automate in the first place, the more additional tasks can be automated. The more you automate upstream, the more you can automate downstream.
Insurance Automation Pitfall 2:
Merely measuring hours of benefits
This pitfall is similar to Pitfall 1. You need to quantify the benefit properly at the outset. But how?
The most common response is also the most misguided: “Hours saved.” When embarking on their automation journeys, insurance carriers, brokerages, and agencies will often add up the hours saved for each discrete task that’s been automated.
This zoomed-in (dare we say “myopic”?) view misses the big picture; it overlooks the ability of your digital workers to help your entire organization to scale. If you’re only counting hours saved on specific tasks, you’re missing the broader benefit picture.
Don’t fall into the trap, then, of simply counting elements like keystrokes or mouse-clicks re-couped. You need to, instead, quantify the ROI, taken together, for all of your digital workers combined.
Automatable Platforms
Which platforms—core and ancillary—can be automated in insurance?
When you unleash digital workers on your insurance organization’s processes and activities, you’ll be able to use them on virtually every system you currently use, both core and ancillary. These include your agency management system, CRM, claims-processing systems, contact-center systems, HRIS, and others.
Digital workers don’t care which brand or vendor you use, either; they’re completely platform-agnostic. They don’t care how you use the systems you use, or how they’re combined.
Want proof? Look at some of these brief videos from The Lab:
The Lab's You Tube Channel of Automation Demos
Policy-renewal and lapse notification processing
Specialty insurance coverage application automation
Policy cancellations automation

Independent adjuster (IA) report-processing automation
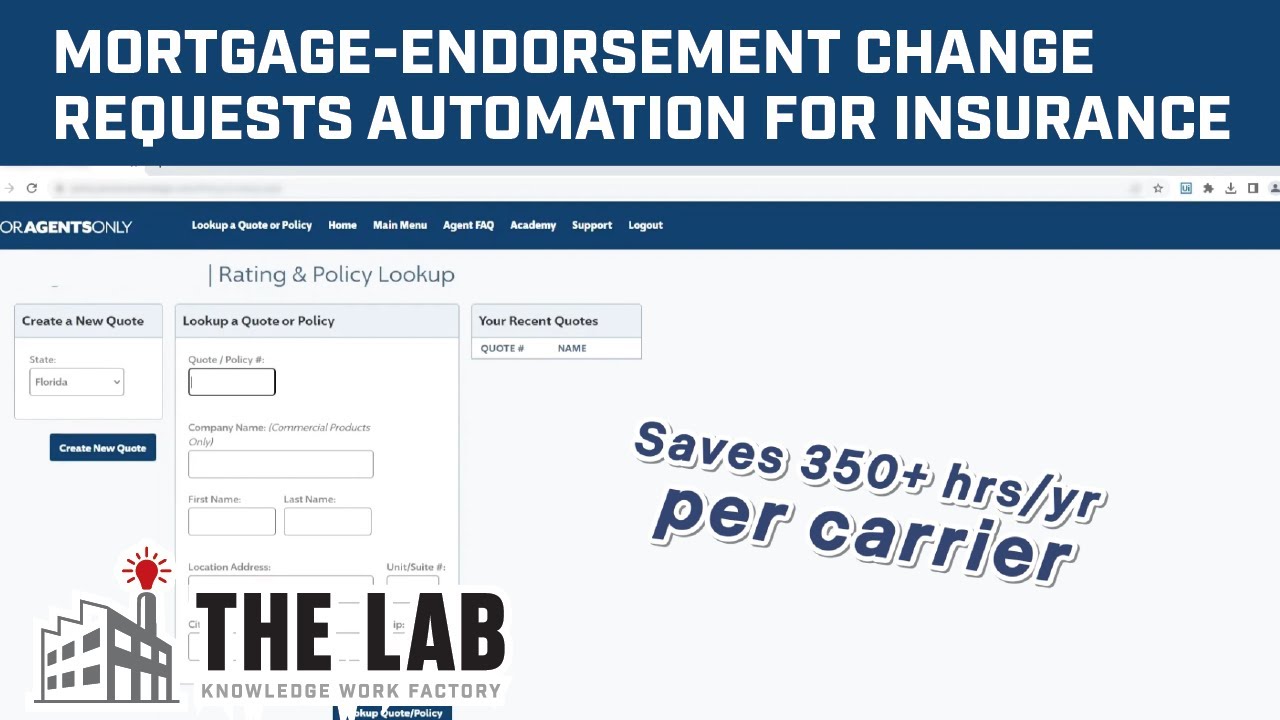
Mortgage-endorsement change-request processing automation
Want to see more?
Check out The Lab’s YouTube channel. We’ve got scores of real, anonymized automations for actual clients, including this entire playlist of automations (and data intelligence) specifically in insurance. Each video is only about three minutes long; you’ll find them engaging and informative.
Best Practice Automation Integration Step-by-Step
How can insurance executives follow best practice for introducing automation in brokerages, carriers, and agencies?
The Lab has compiled and honed a four-step process for developing and implementing, and then managing, automation and digital-workforce onboarding at your insurance organization. It works in just six months. Of all the approaches out there, it’s the established best practice.
We’ve listed those four steps below. And for the last one, we’ve also included a deep dive process for agile automation development. It accelerates the process, and makes sure that your automations will perform as advertised when they’re deployed in your insurance business.

6 Month Implementation
What is the 6-month, 4-step process for using best practice to bring automation and digital workers to insurance businesses?
Each step has its own responsibilities and end products:
1. Confirm your existing work activities
Responsibilities:
- Finalize all insurance volumes and timing
- Complete all required work-effort concentration
- Quantify the automation potential in insurance
End products:
- Map the effective “Work Effort Concentration”
- Create your insurance automation blueprint in MS Power BI
- Build the insurance automation capacity model in MS Power BI
2. Complete the design of the future state
Responsibilities:
- Tweak the future state design for automation in insurance as needed
- Gain consensus on the automation priorities in your insurance business
- Confirm all of the standardization prerequisites in insurance
End products:
- Finalized future-state insurance automation process map
- Prioritized improvements for insurance automation
3. Make sure all data and processes are standardized
Responsibilities:
- Apply all process and data standards for insurance automation
- Create the proper KPI definitions and goals for the automation initiative
- Complete the scoping and setup for the onboarding of digital workers and automation in insurance
End products:
- List of full standardization improvements e.g., business rules, checklist, and so on
- Management dashboard array built in MS Power BI
- Insurance automation scopings and complete automation use-cases
4. Start automating the actual work activities
Responsibilities:
- Finish the list of automation prerequisites
- Build out the initial automations
- Test the automations
- Deploy them
- Hand them off
End products:
- Automations and digital workers using RPA, AI, and data analytics
- Automation in insurance documentation (code “run book,” and so on)
Best Practice Development Step-by-Step
What is the agile development best practice for automation in insurance?
The integration step above—that is, “Start automating the actual work activities”—can be broken down into eight component parts; we know how to do this, since The Lab helps you to build your automation and digital workforce in insurance.
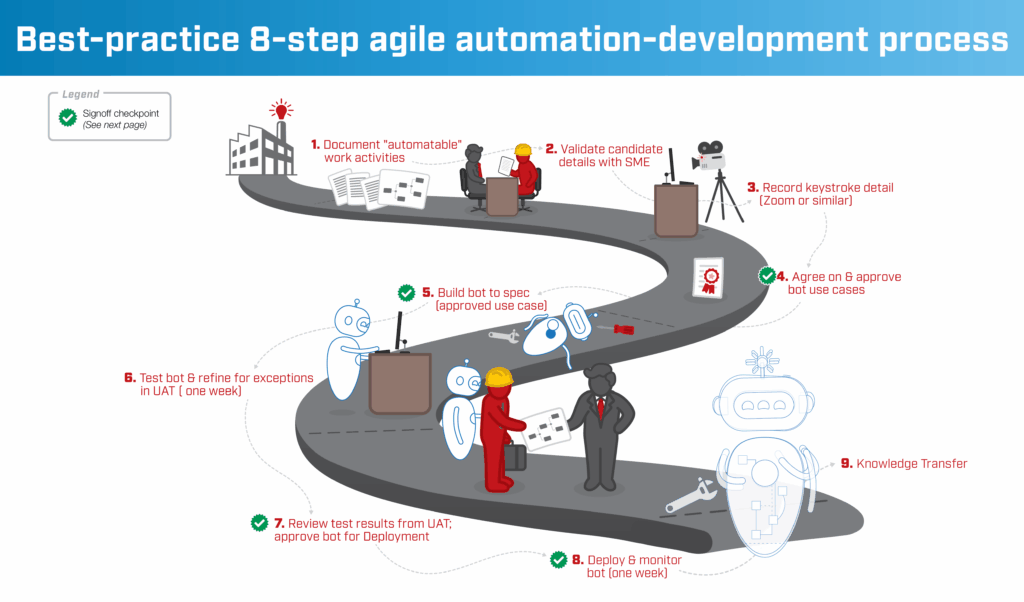
8 Steps in Detail
1. List all work activities which can be automated.
Using the future state map you already created, along with The Lab’s insurance automation catalog, document all “automate-able” work activities. Our Structured Discovery™ process will help to uncover the most valuable insurance automation options.
2. Check those options against your SME’s feedback.
Review the identified automation candidate with the subject matter expert performing the work, to confirm how it’s currently being done… and how it can be automated atop existing systems.
3. Capture individual keystrokes.
Yes, it actually needs to get documented and described, by the SME, at this level of detail.
4. Finalize the use-cases to automate.
Agree on the future state requirements. Document and confirm all specs and details.
5. Construct the automation, per agreed-upon specs.
Using the approved use case from the fourth step, above, build the prototype bot (or automation/digital worker). Run a demo to generate more requirements for its operation.
6. Perform UAT, uncover exceptions.
User acceptance testing or UAT should be performed for a week, as you look to test, refine, and define exceptions.
7. Use UAT results to ready for bot deployment.
Refine the way in which the bot handles exceptions (things it can’t process on its own), based on the previous UAT results. Once done, approve the bot for deployment.
8. Deploy the automation and monitor its performance.
Hand off the newly completed digital worker to the business and to IT. Monitor its performance for a week.
Insurance Automation Challenges
What are the three biggest pitfalls when automating insurance operations?
Automation Acceleration
How can you ensure that automation in insurance gets implemented quickly?
Certainly, you’d prefer a fast pace over a slow one. You want more digital workers and automation in insurance, not less. But how?
The two keys to success are executive sponsorship, along with agile program management. But this isn’t just any initiative; it needs finesse. Never refer to it as, say, “an IT automation project.” Rather, characterize it as “Onboarding a digital workforce into our insurance organization.”
Automation Sponsorship Requirements
How should executives treat sponsorship of automation projects in insurance?
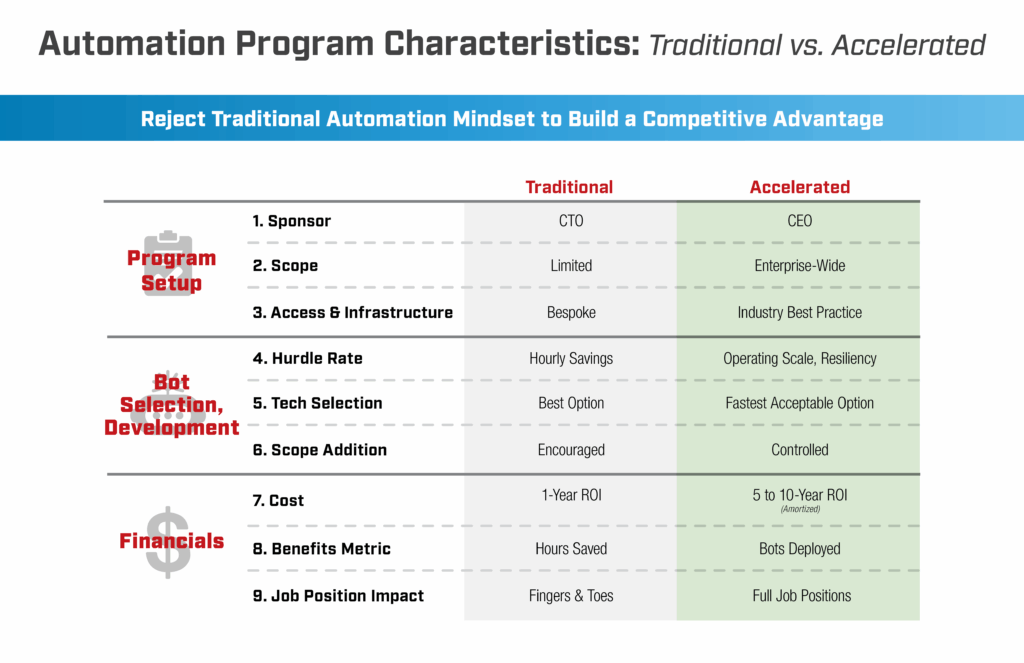
In order to ensure agile program management and effective executive sponsorship, leaders need to:
- Provide aggressive sponsorship
o Put focus on “strategic value” vs. “hourly savings”
o Discourage last-minute adjustments and other forms of scope-creep
o List clear goals
o Provide incentives for automation deployment - Select automations quickly
o Perform fast feasibility reviews for identified automation candidates
o Select digital workers to onboard in surges of at least ten per surge
o Confirm those selections with SMEs; adopt a lather-rinse-repeat cadence - Assign dedicated resources
o Appoint single, dedicated points of contact
– Business SMEs
– IT
– Project management
o Hold teams accountable to 24-hour turnaround - Nip development delays in the bud
o Complete and fulfill system-access requests
o Limit UAT and hypercare to one week apiece
o Avoid the tendency toward over-documentation
Automation Benefits
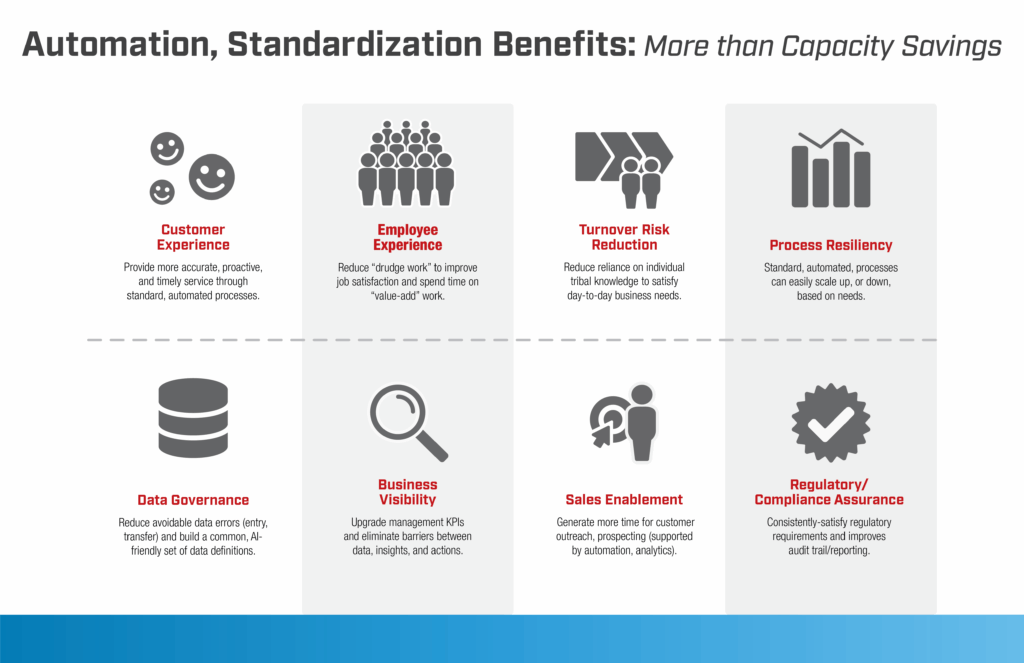
What are the top 8 benefits of automation in insurance?
Beyond the substantial cost savings, there’s a raft of benefits that comes from bringing automation, AI, and digital workers into your insurance organization. These include:
- Insurance Automation Benefit 1: Better employee experience. When you automate activities in your insurance brokerage, carrier, or agency, you increase job satisfaction by eliminating drudgery. Team members will be able to spend more time on value-added work. Consider this one example: How much do your workers enjoy cancelling policies? Watch this three-minute video from The Lab to see this kind of digital worker in insurance in action.
- Insurance Automation Benefit 2: Improved policyholder experience. Your policyholders will enjoy more proactive, timely, and accurate service, thanks to your automated, standardized processes.
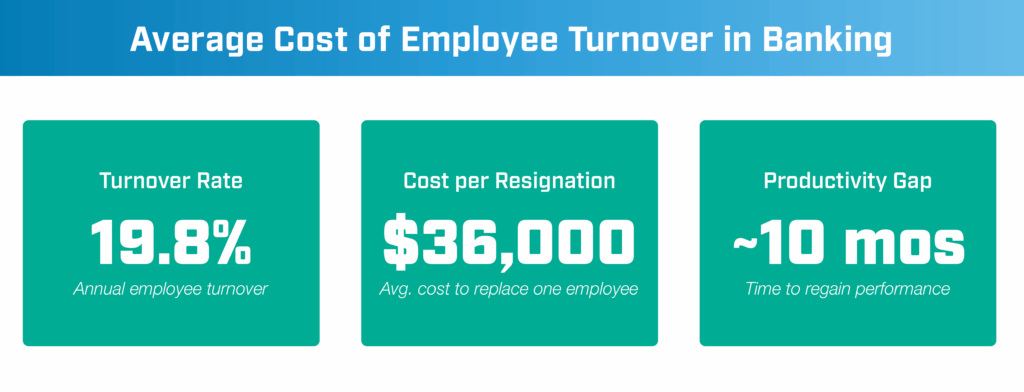
- Insurance Automation Benefit 3: Less employee turnover—and risk therefrom. Why keep relying on tribal knowledge and rules-of-thumb within the ranks? Introducing automation in insurance eliminates this virtual crutch from daily operations and policyholder service.
- Insurance Automation Benefit 4: Improved governance of your data. Build an AI-friendly set of common data definitions—and watch your avoidable data-entry and -transfer errors go away.
- Insurance Automation Benefit 5: More visibility into operations. Along with automation and the onboarding of digital workers in your insurance operation, you’ll enjoy upgraded executive and management KPIs. No longer will you have roadblocks between data-driven insight and action.
- Insurance Automation Benefit 6: More resilient processes. Don’t suffer through painful layoffs or frantic surge hiring. When your processes are standardized and automated, they simply scale up or down, based on your insurance business’ needs at the time.
- Insurance Automation Benefit 7: A newly empowered sales force. Give your sales reps more time for policyholder outreach, cross-sell, and up-sell activities. Free their time for prospecting. It’s all possible when they’re supported by market analytics and automation.
- Insurance Automation Benefit 8: Increased regulatory compliance. Insurance is a heavily regulated industry. With standardized processes and automation, you’ll have better and more consistent processes, and improved audit trails and reporting.
Making It Stick
How can insurance executives make sure that automation benefits persist?
The key to ensuring the longevity of the benefits of automation in insurance is superlative data. But guess what? You already possess it.
It just needs to be tailored for automation. When it’s in a standardized model (where it’s been tagged for clarity and clearly defined in a glossary), you can, for example, monitor your human and digital workforce in impressive new ways:
- Provide workers and their managers with precise, actionable, data-driven insights. No one will struggle trying to understand the data.
- See almost (or even actual) real-time performance of your workers: digital and human alike.
- Prevent and reduce risk: Proactively execute using patterns and predictions.
- Automate more activities downstream.
The Lab has published another explainer article on Data Intelligence, Analytics & Executive KPIs; it provides a deeper dive into this specific topic. And if you’d like any more enticement to read it, consider this: With The Lab’s templates, this kind of data-driven transformation can be implemented in your insurance carrier operation, brokerage, or agency in as few as 6 months.
Automation Support
What kinds of ongoing support for digital workers in insurance are available from The Lab?
“What happens after you leave? I’m not positive we can maintain this insurance automation on our own.” This is a common question posed to The Lab by insurance executive sponsors.
Throughout the insurance-automation project, The Lab works directly with your team; this way, they’ll learn, firsthand, how to support it in the future. Still, they can’t possibly be expected to possess the same level of expertise that our team does. So The Lab offers multiple kinds of client-friendly automation support, going forward:
- Automation preventative maintenance. If your insurance operation is faced with major system updates or changes, they could impact how your digital workers use them. In these instances, The Lab can rapidly assess the situation, providing guidance (including instructions, if warranted) for re-training your digital workforce. We can provide regularly-scheduled routine automation performance audits, too.
- Automation break/fix, i.e., rapid repair. Digital workers typically need about an hour of maintenance each month. The Lab offers same-day fix services—and these come with zero long-term commitment or retainers. Simply pay as you go.
- Automation training support. As we’d mentioned earlier in this article, there are many training materials that are actually available for free. The Lab has curated the best of these to recommend to your insurance organization so you can up-level your skills and capabilities ASAP. In short order, your own developers and team will be delivering complete automation support.
- Core technology changes (ERP, agency management system, etc.). Every once in a while, your insurance business may introduce broad changes to your core or ancillary systems which necessitate the re-training of your digital workers. If core systems are being swapped out, let The Lab assess the impact on your operations, provide a quote, and get started right away.
Contact The Lab
Automate your insurance carrier operation, brokerage, or agency/MGA/MGU today with The Lab
The Lab has helped insurance C-suite executives, their internal business and technology leaders, and operational-excellence teams to automate their enterprises to realize quantifiable results, while delivering on large-scale transformation initiatives.
Our proven comprehensive solutions and services—underpinned by our Knowledge Base containing 30-plus years’ of template-ized, re-deployable client-engagement IP, along with our patented Knowledge Work Transformation™ methodology—can automate your insurance business in as little as six to 12 months.
Ready to automate your insurance carrier operation, brokerage, or agency? To book your screen-sharing demo, call (201) 526-1200 or email info@thelabconsulting.com today.