What is robotic process automation in health insurance?
Robotic process automation as applied to the health insurance industry uses automated software applications to streamline processes and reduce the amount of human labor needed to process health insurance paperwork, such as claims. Applications like Blue Prism and UiPath, when introduced as part of a robotic process automation (RPA) solution, can significantly simplify the required work and skill in health insurance processes. In the past, health plan automation occurred at the level of computer code, but with health insurance RPA, it can now occur at the keystroke level without any conventional coding. When properly configured, RPA knits together mainframe fields, cloud-based software fields, and desktop applications like Excel into a single, streamlined, standardized, and automatic process.
Although it functions like an Excel macro, RPA in the insurance industry is different in an important way. Unlike Excel, it can copy and paste information across multiple different applications and platforms from legacy mainframe to leading edge cloud-based apps at the desktop use level.
You might be thinking that “robotic” isn’t a good term when it comes to health insurance.
Don’t be misled.
In the health insurance claims realm, RPA does not refer to the idea that robots are making high-level decisions. Quite the contrary. RPA insurance use cases involve automating the most simple, repetitive administrative and clerical actions at the keystroke level. Think of the relatively mindless, repetitive tasks of copying and pasting data from one application to another. Automating these simple, repetitive processes frees up your health insurance claims staff to do more engaging, interesting, and important higher-level tasks, letting the computer do what it does best—and with greater speed and accuracy, too.
Some people call what RPA does in health insurance companies the “last mile” of process automation, in that robotic process automation in health insurance addresses the gap between different applications that were left after large system implementation were completed. In most health insurance claims departments, implementations like Oracle Health Insurance Claims Adjudication, Plexis, and Pega fall short of the goal of straight-through processing – even though these were sold as being able to do so. With health insurance RPA, the focus is on the micro-task or keystroke level, integrating processes that the big systems did not adequately address – or were never able to actually do.
Taking full advantage of the benefits of RPA in the insurance industry, means understanding that the real economies of scale from robots are only realized when there are many, standardized, repetitive processes and large scale to automate. Most health insurance companies have very few standardized processes outside of legacy systems, especially when it comes to the manual work-arounds.
So, most will benefit from the services of The Lab to first analyze and standardize their manual work. Depending on the department or region, there may be non-standard formats for submitted data, due to lack of guidelines and standards. Lack of standard processes can prevent up to 60% of potential RPA from being implemented. It’s important to do the up-front analysis to determine which jobs and which processes to automate, in order to improve your ROI for the project significantly. Moreover, it’s important to find a partner who can pilot their solution for you on a limited basis before scaling up.

Benefits of RPA in health insurance claims
RPA is currently seen as the final frontier, and the last step, for automating health insurance operations. Health insurance companies are rife with repetitive minute-level administrative tasks and manual processes outside of legacy systems, so if those tasks and the work can be standardized and automated, labor costs are reduced, and efficiency significantly goes up. Job positions can be improved, freeing employees from mindless, repetitive tasks, and decreasing the chance of error in the process.
Benefits of RPA in insurance use-cases being implemented include:
- 50% reduction of health insurance claims processing costs. Robots assist full-time employees by getting rid of time spent on repetitive processes and automatically transcribing information from various sources across multiple systems.
- Increased claims processing speed by up to 70% by automatically validating customer data and inputting insurance claims submission data submissions across different systems.
- RPA insurance processes can run 24/7/365. Robots don’t need overtime pay, health insurance, nor do they quit on you.
- Reduction of error rates in health insurance claims processes by 60%. Health insurance RPA updates personal and account details across systems to facilitate claims processing and can automatically identify policy premium discrepancies.
- Decreased policy issuance time. Health insurance robots handle data entry of new customer onboarding, gather and move customer information across various systems, and generate premiums in less than two minutes.
- Health insurance RPA maintains regulatory compliance up to 100%. Robots maintain running log of actions and conduct automated compliance checks.
A detailed RPA use case in health insurance claims
A real-life RPA in health insurance claims processing example will help simplify what seems exceedingly complicated. Let’s say that you want to reduce data transcribing and reconciliation work required to process new inbound claims from a doctor or hospital for a procedure.
The current pre-RPA health insurance claims process typically goes as follows:
- Receive a PDF claim form through email from the customer
- Manually attach the claim form to the claim processing system
- Manually search to check to see if the person requesting a claim is a customer in the claim processing system
- Then manually copy and paste the claim form data into standard fields in the claim processing system
- Manually notify the customer through Outlook email that their claim is being processed
Wait a minute. That’s a lot of manual work for a company that has been sold core health insurance claims systems that offer “straight through processing” 4 times by now, right? This is the reality of all large health insurance companies today. But, have no fear, RPA is here to bridge the gaps.
Now let’s review the claims process after RPA has been layered on top.
- RPA opens the email application, and the .pdf file which contains the claims form data.
- RPA copies the .pdf fields from the form and pastes them into the web-based health insurance claims document management system while attaching the actual .pdf form automatically.
- RPA searches the claim processing system to validate that the claim submitter is a customer by copying the name from the invoice and searching in the claims processing system
- RPA attaches the invoice to the claims processing system.
- Finally, the RPA sends the claim to the back office for approval while it creates an automatic Outlook email for the customer notifying that the claim is being processed.
The key steps that the health insurance RPA solution handled in this use case automatically are as follows: UiPath logged into the application, navigated the necessary screens automatically to find the needed fields containing the information, and copied and pasted the information into the new document in the DMS and claims management system. Insurance RPA also controlled the applications involved at the level of the mouse and keyboard, moving the mouse to the appropriate fields and entering data and/or keystroke combinations as needed. It sounds like magic, right? It almost is – but you have to put in the front-end analysis work and process standardization to get it to work. We can help you with that.
Steps to implement robotic process automation use cases in health insurance claims
Scope the health insurance RPA project to identify manageable use cases
While it’s true that not all workstreams are created equal, some are certainly better candidates than others for your first health insurance RPA project. Does the work that you are considering for RPA require a lot of human estimation? Then it’s probably not a great candidate for RPA. Health insurance claims processing, with its repetitive work, is a great candidate for RPA. The first step, scoping the project, means you must identify a small, manageable list of processes that would benefit from being automated. Ideally, these must be repetitive, clerical, administrative tasks that require little human intervention and that occur frequently. But – what if you have no standard processes for manual work? More on that a little bit later.
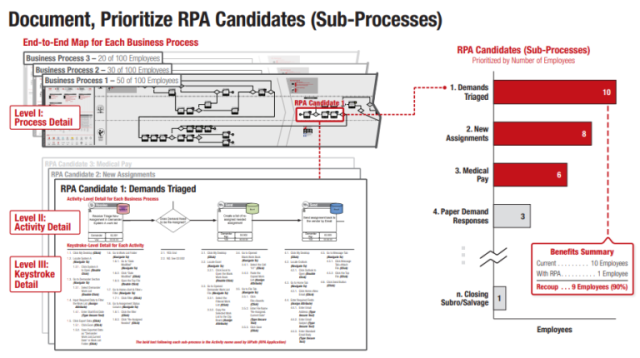
One way to minimize risk and maximize buy-in is to start with a pilot scope, two or three work streams that have simple, repetitive steps performed on a frequent basis. Don’t attempt to automate the entire company at once. You have to start small before thinking big and rolling out at scale. Success at a small scale will allow you to gain supporters and invest in rolling the project out to the entire group or department. It also lets you learn the tough lessons you will encounter at small scale. It’s much easier to right a canoe when compared to an aircraft carrier. So, do yourself a favor and start with a manageable scope.
Determine baseline health insurance claims operating cost to calculate the total benefits realized from RPA implementation.
Once you have determined the scope of your pilot project, it’s time to determine a baseline cost of your health insurance claims group. You will need this information to determine the total benefits you’ll realize from RPA in claims processing — your before and after, if you like. How much money you saved. Measuring your initial operating costs and the comparing them against your reduced operating costs is an essential step to keeping the project going. You want to prove the results of the process standardization and the RPA roll out.
How do you determine a baseline cost for an RPA insurance project? Take the scope you have outlined above and go over to the HR department to work with them to figure out what each employee in the department costs, fully loaded with benefits and everything. If they refuse to share this information with you, you can find reasonably accurate salary info of various health insurance claims positions on websites like Indeed and Glassdoor. You can then reverse engineer the baseline operating cost from there.
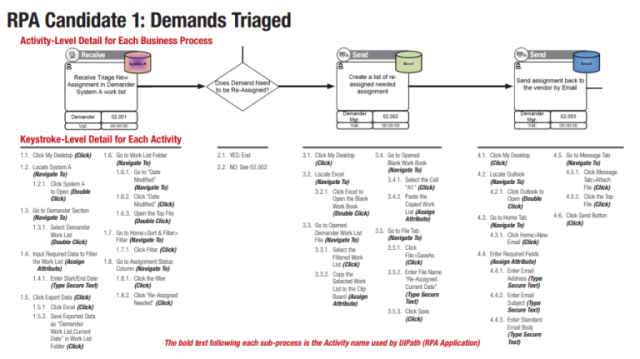
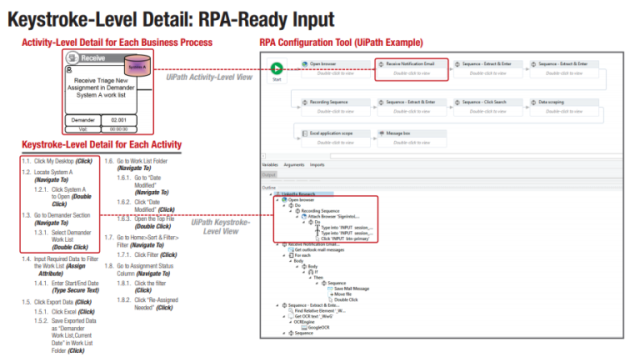
Analyze current state health insurance claims processes to document robotic process automation opportunities – all the way down to the mouse click level
Let that sink in for a moment. The mouse click level. Sounds like a lot of work? Well, it is. Let’s get to work.
Once you have collected your baseline cost data, it’s time to map the processes—that’s how you’ll identify opportunities for RPA in the health insurance claims operations. You can use process mapping software like Microsoft Visio to represent the processes in scope visually. It’s important to use a stencil such as the BPMN 2.0 stencil (Business Process Model and Notation) — which is the standard that all the IT professionals are using. That way, you’ll save time later when handing off the workflows to the team that implements the automation solution.
The only way to make this actually work is to observe a health insurance claims worker at their desk for a few days, notebook or laptop in hand – or lap. You will need to take extremely detailed notes of every keystroke and mouse click within all the applications you would like to automate using RPA. Organizations like The Lab will do this type of “day in the life” observation for you, utilizing such screen-sharing software as GoToMeeting or WebEx, or even face to face if you prefer. Many organizations prefer the former route, since remote observations via screen-sharing significantly lower the project costs.
However you choose to perform your observations and take your notes, it’s important to observe multiple health insurance claim workers for a few days, one at a time—enough to get a good sample size. That way, you’ll have enough reliable information to generate the RPA improvement business case with accuracy. A good rule of thumb is to observe 50-500 workers and then scale up.
Standardize insurance claims processes before or during health insurance RPA implementation – but not after
Why is standardizing the workflow and procedures before or during an implementation of health insurance RPA so important? Well, let’s think about it for a second.
When a robot on a factory floor is welding pieces of metal together, it can do this job very quickly and with minimal errors because the process was standardized before the robot was deployed. The robot always welds spot A before spot B, and welds spot B before it welds spot C, allowing it to move quickly and precisely. In fact, all the robots on the assembly line floor doing the same job are programmed to weld spots A, B, and C, in the same order, allowing them to run the same software program, and moving not just with great speed but also accuracy.
Similarly, you must standardize the workflow and procedures for processing a health insurance claim before RPA is implemented. That way, you’ll realize the maximum benefits of scale. While saving a few minutes out of one claims processer is wonderful, the benefits will fall short unless you roll out the work to the whole group of health insurance claims examiners in a uniform way. If Mary copies and pastes data in a different order than John does, and Sue copies and pastes the same data in yet a third order, you’ll want to choose one standardized way of doing the job before or during RPA implementation. Waiting till afterwards will only increase your costs, and you’ll fail to realize all the potential benefits that RPA in insurance claims processing has to offer.
Hire an insurance RPA vendor to implement – or do it yourself if you have the time – but talk to us first
Health insurance RPA software is not going away anytime soon—in fact, it’s becoming more popular all the time. One question you might ask is whether to hire an RPA vendor to implement it, or whether to do it yourself, if you have the skills and the time. It’s your classic “make or buy” decision. Before making that choice, though, why not check out the community version of UiPath — that way, you can understand it and test it out.
According to a February 2018 Medium article, “as with traditional automation solutions, one of the most obvious benefits of RPA lies in reducing the cost of manual processing. When compared to no automation, RPA costs one-fifth for on-shore full-time employee (FTE) and one-third for offshore FTE. RPA applications can also reduce the error rates by 20% and relieve employees from tedious tasks, enabling them to focus on more productive activities.”
Whether you decide to hire an RPA vendor like The Lab, or do it yourself, you can realize significant gains towards increasing your auto-adjudication rates by following these recommended steps. Contact us if you want to get a head start today.